Driving Progress: The Crucial Role of Open Source in Public Transportation Technology
By Milo Green
In the era of rapid urbanization and the climate crisis, public transportation systems have become vital for ensuring sustainable mobility and reducing the impact of congestion and pollution. One unsung hero behind the scenes of modern public transit is open-source technology. When a technology is open source, it simply means that software has been produced in such a way that anyone can inspect, modify, and enhance it. This is important because it represents open collaboration, which many advocates believe helps facilitate greater public trust in the software while improving functionality and sustainability. Both federal and state agencies, such as the CA Department of Technology have adopted strong open source first mandates for software solutions developed or acquired using public funds.
Our goal at Compiler is simple - to help government agencies meet their strategic goals and better serve communities. We do that by providing customized solutions and impactful consulting services to improve IT workflows within organizations. One key component of this is working on code that is open source. We feel strongly that software and code developed using tax dollars should be produced as open source wherever possible, as this increases transparency, reduces opportunities for vendor lock-in, and delivers better and more cost-effective results to the public.

Some of the benefits of open-source software development include:
-
Cost Efficiency: Governments have long used models of collective purchasing and procurement; open source is another take on this proven model. One of the most significant advantages of open source in public transportation technology is cost efficiency. By making software and hardware solutions freely available to developers and transit agencies, the financial burden associated with proprietary systems is substantially reduced. This enables more agencies, especially those with limited budgets, to implement cutting-edge transportation technology.
-
Collaboration and Innovation: Open source fosters collaboration among a diverse group of developers, transit authorities, and communities. This collaborative ecosystem encourages innovation and rapid development. It allows for a constant stream of improvements and new features that can be tailored to meet the unique and ever-evolving needs of different cities and regions. Investments in a new feature by one agency are available to all other users of the software.
-
Transparency and Security: Open-source technology is built on transparency, which is crucial for public transportation systems. It ensures that the code and data used in transportation systems are visible, allowing for better security, easier debugging, and protection against potential vulnerabilities or malicious attacks.
-
Accessibility: Open-source technology promotes accessibility for all. It empowers transit agencies to create user-friendly interfaces, improve passenger experience, and provide valuable information about routes, schedules, and services. This accessibility is particularly beneficial for individuals with disabilities.
-
Scalability: Public transportation systems often need to scale their operations to accommodate population growth and changing demands. Open-source technology provides a flexible framework that can be adapted to meet the evolving needs of existing transit infrastructure that typically has more constraints around how and how quickly it can change.
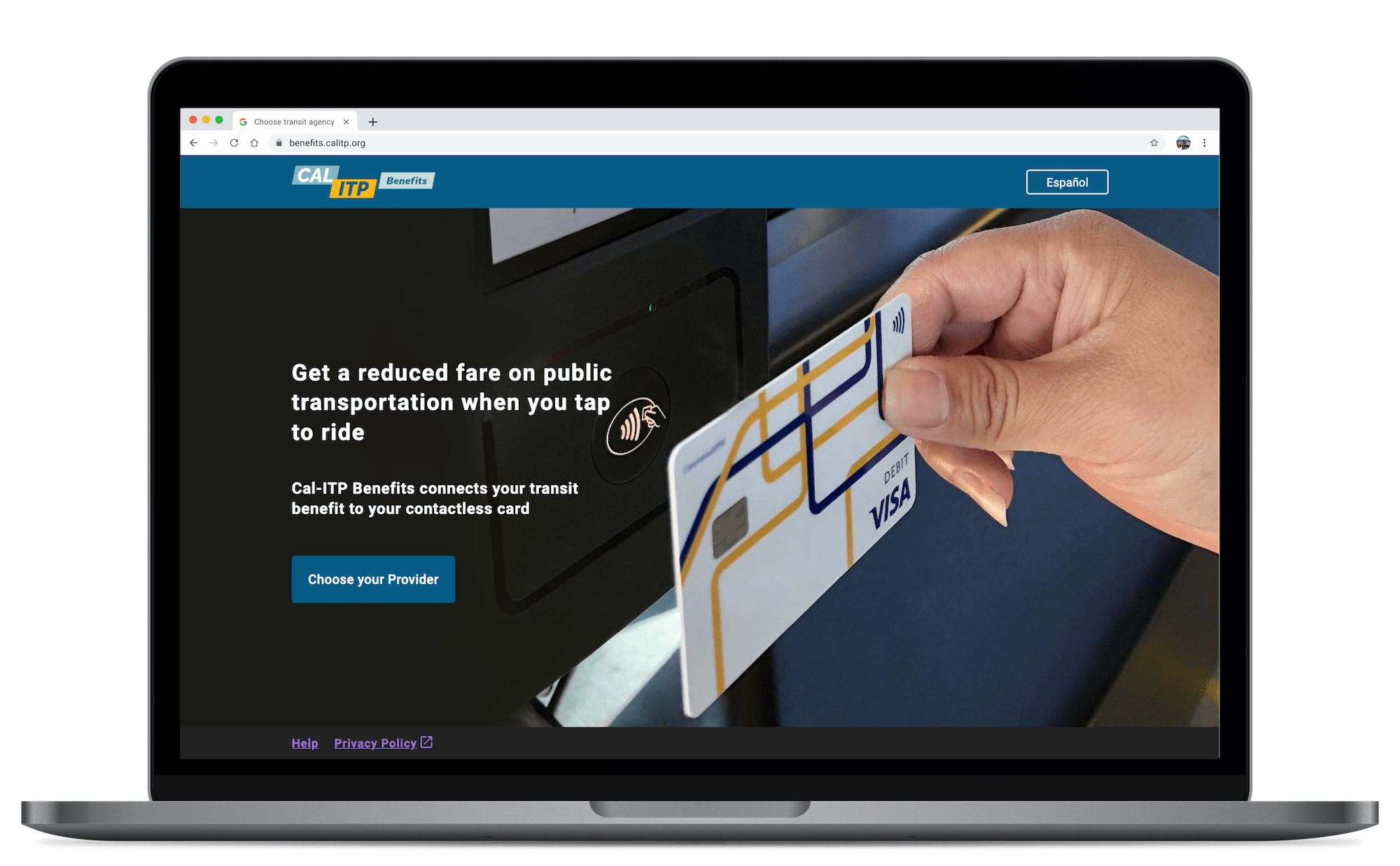
We feel that open-source technology is a driving force behind the next evolution of public transportation systems. It is cost-effective, fosters innovation, ensures transparency, promotes accessibility and allows for scalability. With open source, cities can build smarter, more efficient, and more sustainable transportation networks that benefit everyone. Embracing open source in public transportation technology is not just an option; it’s necessary for bettering our cities and the planet. For example, Compiler’s work on the Cal-ITP Benefits App has been entirely open source, and we’re proud to say that this approach has made the project stronger, more sustainable, and more effective at serving communities throughout California.
Additionally, a wide variety of Metropolitan Area Planning Council’s projects are open source. Check out this list for more examples of great, innovative, open-source projects.
For further information on Open Source development, check out The Intergovernmental Software Collective.